
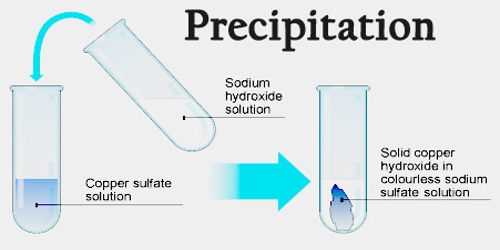
Solubility and precipitate reactions are very important to many chemical processes. They can tell us unknown compounds, and create pure metal salts by removing impurities through precipitation. After centrifuging, it was AgCl (silver chloride), showing that the precipitate had formed due to the insolubility of silver chloride in water. In one lab class, silver nitrate and sodium chloride were mixed and an unexpected white solid appeared. Spectator ions, that don’t take part in the reaction but stay in the solution, must be considered when balancing chemical equations for precipitate reactions. The solubility table can be used to predict whether a compound will dissolve or form a solid.įor example, nitrates are usually soluble, while iodides have some exceptions. It’s vital to know that not all molecular compounds will form a precipitate. This is called a precipitate and is caused by solubility rules. When certain ions are in an aqueous solution, they may react to form a solid which cannot be dissolved. Image Credits : Wikipedia Solubility and the formation of an insoluble precipitate Writing the correct equation type also helps to highlight certain parts of the reaction. To summarise, understanding solubility guidelines is important for predicting whether a precipitation reaction will happen. To accurately write out a precipitation reaction equation, different types of equations such as molecular equation, ionic equation, or net ionic equation are used. They stay unchanged throughout the entire process and are not relevant to the formation of the precipitate. Spectator ions can be present in the solution during a precipitation reaction, but they don’t take part in the reaction. Solubility guidelines can be used to work out if a particular ion is soluble or insoluble in water. Not all ionic compounds will form a precipitate when mixed together in aqueous solutions. If one of these compounds is insoluble in water, then a precipitation reaction occurs. The reaction is a double replacement, where the cations and anions switch partners to make two new ionic compounds. This precipitate can be separated from the mixture using techniques like centrifugation. Once the precipitate has been recovered, the resulting powder may be called a "flower.A precipitation reaction happens when two aqueous solutions holding cations and anions react and produce an insoluble solid, a ‘precipitate’. A common sedimentation technique is centrifugation.

Sedimentation refers to any procedure that separates the precipitate from the liquid portion of the solution, which is called the supernate. If the particle size of the insoluble compound is very small or there is insufficient gravity to draw the solid to the bottom of the container, the precipitate may be evenly distributed throughout the liquid, forming a suspension. The solid that is formed is called the precipitate. A chemical that causes a solid to form in a liquid solution is called a precipitant.

Here's how it works: forming a solid from a solution is called precipitation. The terminology can seem a bit confusing. They are used for purification, removing or recovering salts, for making pigments, and to identify substances in qualitative analysis. Precipitation reactions serve important functions.The solid that forms via a precipitation reaction is called the precipitate.To precipitate is to form an insoluble compound, either by decreasing the solubility of a compound or by reacting two salt solutions.In chemistry, precipitate is both a verb and a noun.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
